Sodium
What’s the link between: Salt Shaker – Hypertension – Stroke – Heart Disease – Death
It is a well-established FACT that high sodium intake contributes to hypertension (high blood pressure). Hypertension is a strong risk factor for stroke and cardiovascular disease, which are the most common killers of men and women worldwide.
The association between sodium intake and blood pressure is very strong. A recent review of nine studies involving 645,000 participants concluded that sodium intake and cardiovascular events exhibited a dose-response linkage. For every 1 gm (1,000 mg) increase of sodium intake, the risk for cardiovascular events increased by up to 4%.

A high sodium intake also has a negative impact on other health risks, including gastric cancer, obesity, Meniere’s disease and osteoporosis.
The average American intake of sodium is 3400 mg per day, though the recommended amount to consume daily ranges from 1500 mg -2300mg per day. Regardless of your current level of sodium intake, reducing your sodium intake by 1,000 mg per day will improve blood pressure and heart health.
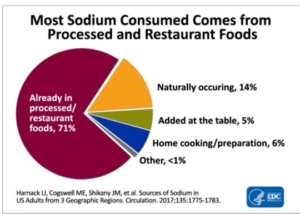
Reducing sodium in your diet is challenging, but not impossible. As a consumer you want to become aware of manufacturer-added sodium by reading labels, as well as the amount of sodium you add while cooking and at the table. Until mandatory sodium reduction targets are implemented for packaged and restaurant foods, you can be sure that many of these foods are contributing significantly to your sodium intake. So, it’s good to be mindful of the foods you choose and the portions you consume.
If you aim for an average intake of 2,000 mg of sodium/day, what would this actually look like? Let’s take a look at the sodium content of foods you may be consuming.
Table salt is a combination of sodium and chloride with 40% of it being sodium. One teaspoon of table salt contributes 2400 mg of sodium, which is more than the recommended intake for an entire day. As an experiment, put one teaspoon of salt in a clear salt shaker and see how long you can make it last. Can you decrease the amount of salt added to recipes by half?
Try to curb your intake of foods that are high in sodium, such as processed meats (deli meats, any meat that comes in a vacuum-packed sealed wrapper, canned meats), cheese, canned vegetables, canned soups, canned tomato products, and pickled foods (pickles, olives, sauerkraut).
Restaurant choices are typically always high in sodium because salt is the most economical seasoning to increase flavor. Minimizing your frequency of restaurant meals will be a very effective way to decrease your sodium intake.
Finally, try to increase your intake of fresh foods, like fresh fruits, vegetables, and meats, all of which have minimal if any sodium. Rely on fresh as much as possible. Fresh produce and fresh meat from grocery stores, as well as produce from farmers markets, and your own garden produce are extremely flavorful and healthy options.
If you have a history of hypertension, or are newly diagnosed with it, consider a consultation with a licensed/registered dietitian to receive nutritional guidance that is specific for you, your lifestyle and your overall health.